
SELECTIVE LASER SINTERING (SLS)
What is SLS 3D Printing?
Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) is a 3D printing technology that uses a laser to fuse powdered materials together, layer by layer, to create three-dimensional objects. SLS is particularly well-suited for producing complex, functional, and detailed parts with a wide range of applications, from rapid prototyping to end-use production. Here's an overview of SLS 3D printing.

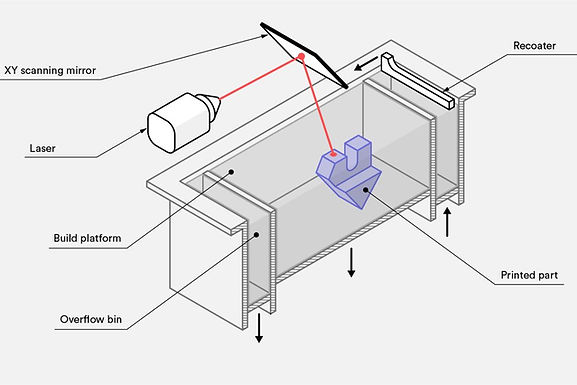
How does SLS work?
-
Powder Bed Preparation: A thin layer of powdered material (typically polymers, metals, ceramics, or composites) is evenly spread across the build platform.
-
Laser Scanning: A high-powered laser is used to selectively fuse the powdered material particles together based on the digital design's cross-sectional slice. The laser scans and sinters the powder according to the design.
-
Cooling and Solidification: As the laser heats the powder, it melts and fuses, forming solid layers. Once a layer is completed, the platform lowers by a layer thickness, and a new layer of powder is spread over the previous one. This process is repeated until the entire object is built.
-
Post-Processing: After printing, the build platform is removed from the machine. Excess powder acts as support, eliminating the need for additional supports. The printed part is then extracted from the powder, cleaned, and often subjected to further post-processing steps like sanding, polishing, or surface treatment.

Cases for SLS 3D Printing
Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) printing is a transformative technology that finds numerous applications across diverse industries. In aerospace and automotive sectors, SLS enables the production of lightweight, high-strength components, from intricate engine parts to custom interior elements. In the medical field, SLS creates patient-specific implants, prosthetics, and surgical guides with precision. Industrial manufacturing benefits from SLS for fabricating tooling, jigs, and production-grade parts. The consumer goods industry utilizes SLS to craft intricate fashion accessories, electronics enclosures, and more. Architecture, education, and research fields leverage SLS for intricate prototypes, models, and materials research. With its ability to produce complex geometries, durable parts, and functional prototypes, SLS consistently proves its worth in revolutionizing design, manufacturing, and innovation across an array of sectors.
Benefits of SLS
-
Material Variety: SLS supports a wide range of materials, including thermoplastics, elastomers, metals, ceramics, and composites
-
No Need for Supports: SLS does not require support structures because the unsintered powder acts as natural support for the part during printing.
-
High Precision and Detail: SLS can achieve intricate details and high precision due to the fine laser spot size.
-
Production-Ready Parts: SLS is used for both rapid prototyping and end-use production due to its ability to create functional parts with good mechanical properties.


Challenges of SLA
-
Surface Finish: The surface finish of SLS parts can be rough, requiring post-processing to achieve a smooth and polished appearance.
-
Equipment Cost: SLS printers and materials tend to be more expensive compared to some other 3D printing technologies.
-
Powder Handling: Working with powder materials requires special handling and safety precautions to prevent exposure and contamination.
-
Powder Removal: Extracting the printed parts from the powder bed can be time-consuming and messy.

